blockchain technology
Understanding Blockchain Technology: Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that securely records transactions across multiple computers. It enables transparency, security, and efficiency, making it an ideal solution for various industries, including finance, supply chain, healthcare, and more.
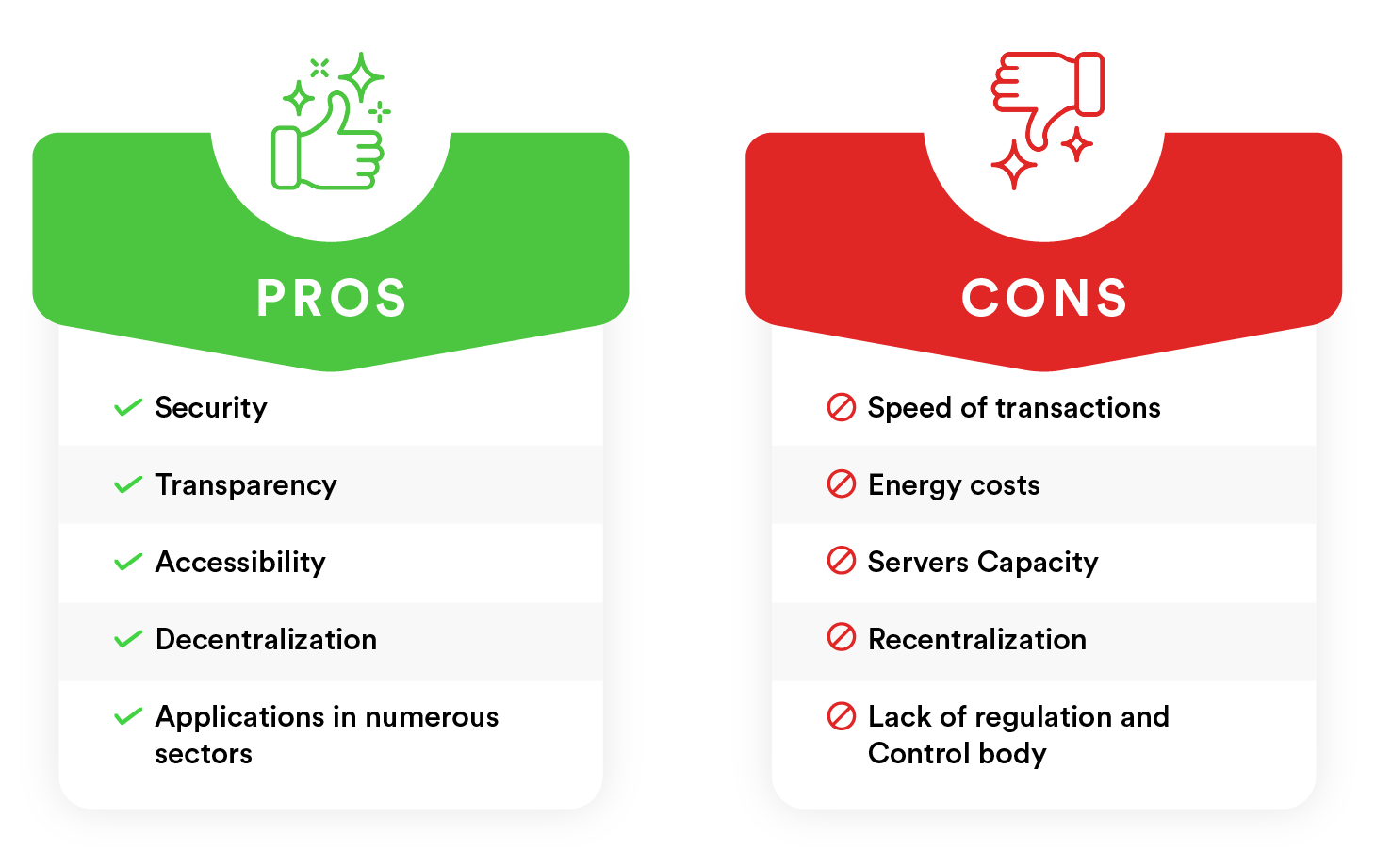
Key Benefits of Blockchain:
- Transparency: All participants have access to the same data, enhancing trust and accountability.
- Security: Data is encrypted and linked in a way that makes it tamper-proof.
- Efficiency: Eliminates intermediaries, reducing costs and transaction times.
Assessing Readiness: To determine if your organization is ready for blockchain implementation, consider the following:
- Understanding Use Cases: Identify how blockchain can benefit your organization. Are there specific processes that could be improved?
- Infrastructure Assessment: Evaluate your current IT infrastructure to ensure it can support blockchain technology.
- Skill Gap Analysis: Assess your team’s knowledge of blockchain. Invest in training or hire experts if necessary.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure you understand the legal implications of using blockchain in your industry.
- Pilot Projects: Start small with pilot projects to test the technology before a full-scale implementation.
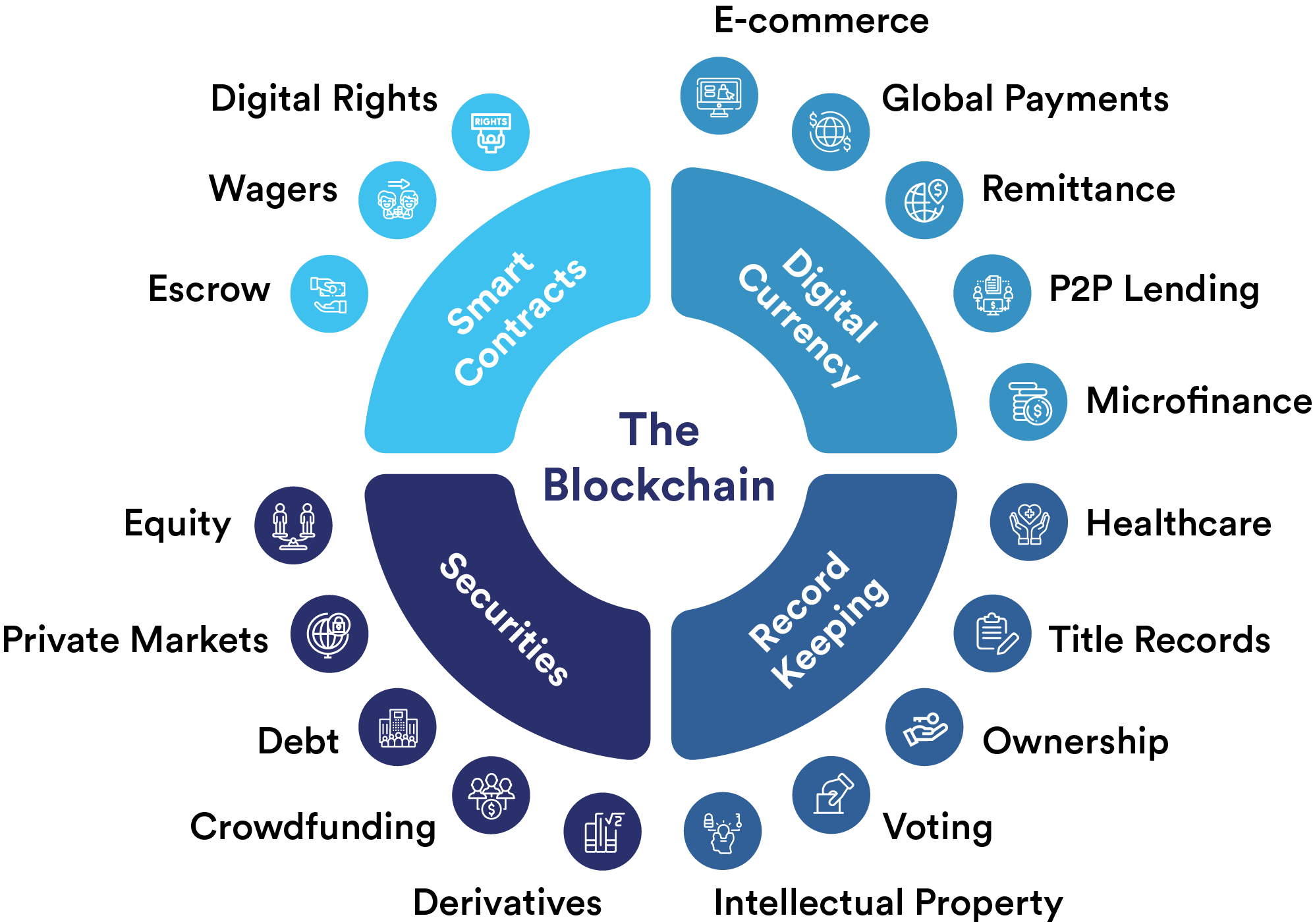
Blockchain Is Used In Any Sphere Of The Society
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing various sectors by providing solutions that enhance transparency, security, and efficiency. Here are key areas where blockchain is making an impact:
Finance and Banking:
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum operate on blockchain, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries.
- Smart Contracts: Automated contracts that execute when predefined conditions are met, streamlining processes in lending, trading, and settlements.
- Cross-Border Payments: Faster and cheaper international transactions with reduced reliance on traditional banking systems.
Supply Chain Management:
- Traceability: Tracking products from origin to consumer, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud.
- Inventory Management: Real-time data sharing among stakeholders improves efficiency and reduces costs.
Healthcare:
- Patient Records: Secure sharing of medical data among providers while maintaining patient privacy.
- Drug Traceability: Monitoring the supply chain for pharmaceuticals to prevent counterfeit drugs.
Voting Systems:
- Secure Elections: Utilizing blockchain for transparent and tamper-proof voting systems, increasing trust in electoral processes.
Real Estate:
- Property Transactions: Simplifying the buying and selling of properties through smart contracts, reducing the need for intermediaries.
- Title Management: Securely recording property titles to prevent fraud and disputes.
Identity Verification:
- Digital IDs: Blockchain-based identity systems that allow individuals to control their personal information and verify their identity securely.
Energy Sector:
- Decentralized Energy Trading: Peer-to-peer energy trading platforms that allow consumers to buy and sell excess energy generated from renewable sources.
Entertainment and Media:
- Copyright Management: Ensuring artists and creators are compensated fairly through transparent royalty distribution.
- NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): Digital ownership of unique assets, such as art or music, providing new revenue streams for creators.
Government and Public Sector:
- Land Registries: Using blockchain to secure land ownership records and prevent disputes.
- Transparent Budgets: Enhancing government transparency by allowing citizens to track public spending.
Education:
- Credential Verification: Securely storing and sharing educational credentials, making it easier for employers to verify qualifications.